ISSCR News

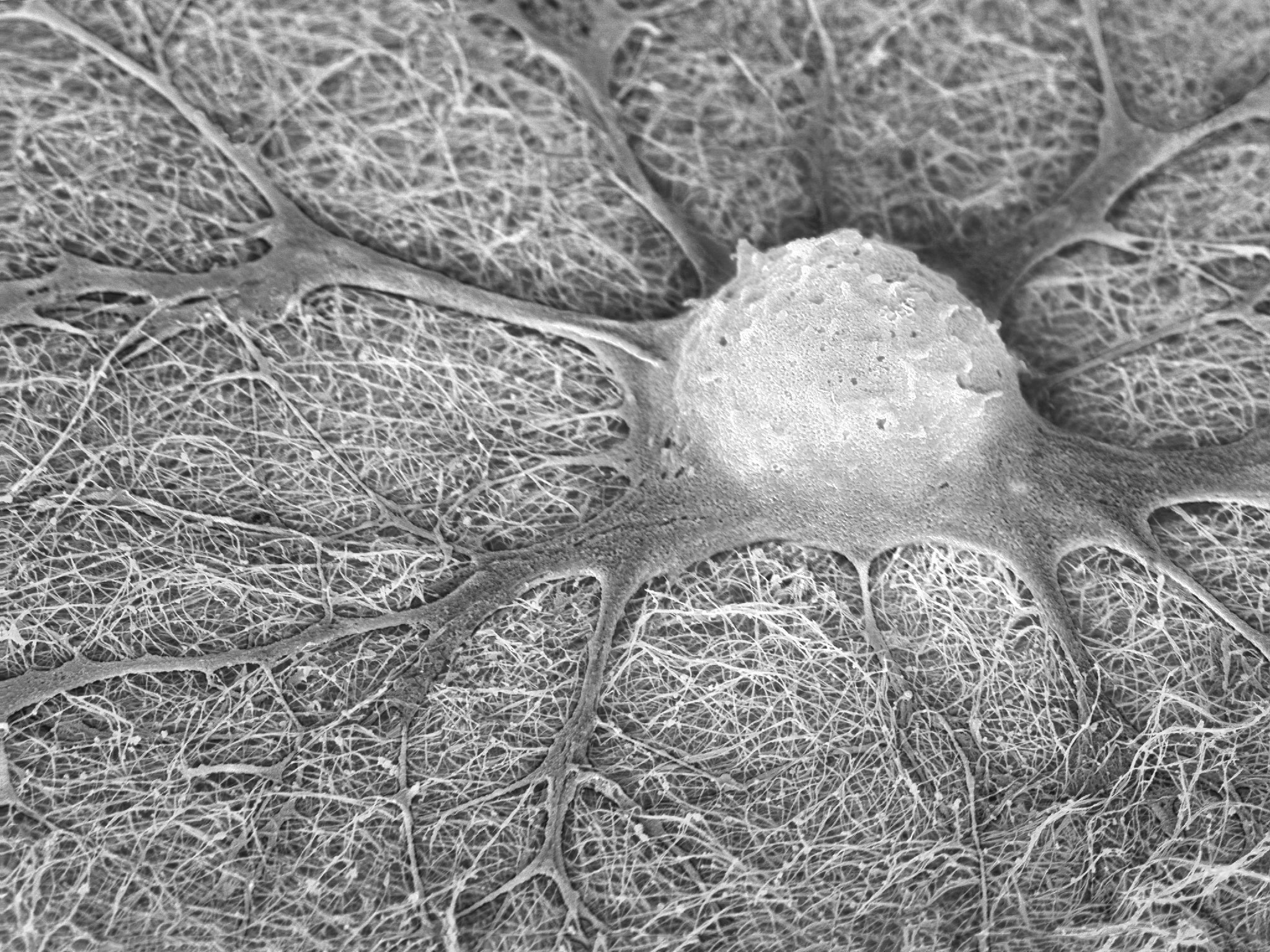
New Podcast Episode. Illuminating hPSC-derived Sensory Neurons
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are transforming the study of biology and disease by enabling scientists to grow large amounts of specific cell types in the lab that were once difficult to obtain. Our guests today focus on improving the derivation and study of sensory neurons, which are sparse and diverse nerve cells near the spine that carry information like pain, touch, or position of the body to the brain. Damage to these neurons or sensory neuropathies, as can happen in diabetes or infections, is estimated to affect millions of people worldwide, yet treatments are limited. To improve the generation of human sensory neurons, the authors developed a genetic toolkit to fluorescently label these individual cells and their subtypes. This approach enables more precise study of these subtypes, their roles in disease, and potentially the development of treatments for sensory neuropathies.

The ISSCR and ASSCR Partner on Joint Travel Award for ISSCR 2026
The ISSCR and Australasian Society for Stem Cell Research (ASSCR) are partnering to launch the new ISSCR-ASSCR Joint Travel Award to support ASSCR student and early career member attendance the ISSCR 2026 Annual Meeting in Montréal on 8-11 July 2026.

ISSCR Guidelines Update Now Available in Spanish
The ISSCR is pleased to announce the availability of the Spanish language translation of the ISSCR 2021 Guidelines for Stem Cell Research and Clinical Translation.

New Podcast Episode. Tuning the X.
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression is an important mechanism in development and disease. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most prevalent epigenetic modifications for RNA and has been shown to play critical roles in processes such as embryo development, cancer, and stress responses. Our guests today investigate how m6A regulates X chromosome dosage compensation to ensure proper balance of gene expression from X chromosomes between sexes. X-chromosome dosage compensation is accomplished through two complementary mechanisms. First, X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) silences one of the two X chromosomes in female cells. Second, the remaining active X chromosome is transcriptionally upregulated so that its gene expression levels are balanced with those of the autosomes, a process known as X-to-autosome (X-to-A) compensation. The authors dissect the distinct contributions of m6A RNA methylation to XCI versus X-to-A compensation across multiple embryonic lineages, providing deeper insights into the epigenetic regulation of early development.

New Podcast Episode. Building a Better Barrier: Modeling the Human gut Epithelium
The human intestinal epithelial barrier comprises diverse proliferative, secretory and absorptive cell types that facilitate nutrient digestion and absorption and protect against harmful environmental agents. The barrier and its function can vary between individuals due to genetic differences thus impact processes such as digestion, drug metabolism, and drug sensitivity. Our guests today investigated the effect of diverse culture conditions on the cell type composition, gene expression profiles, and maturation status of human pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal epithelial cells in three different model systems. Their research provides insight into the relevant conditions and systems for modeling specific intestinal functions and highlights the importance of personalized intestinal model systems.
Receive ISSCR Press Releases
Sign up be a part of ISSCR’s media list. Media Contact: Kym Kilbourne, Director of Media and Strategic Communications
Subscribe to ISSCR News.
Each month, ISSCR delivers scientific, policy, and community to your inbox .
